
by John McCarthy Consulting Ltd. | Nov 1, 2023 | Blog, News
The intention of this blog is to comment on some of the differences between the Industrial & Provident Societies Acts 1893 to 2021 versus the Companies Act, 2014:
Entity size thresholds – the Industrial & Provident Societies Acts 1893 to 2021 contain no concept for ‘micro’, ‘small’, ‘medium’ or ‘large’ entities, as these are all concepts enshrined in Irish company law by the Companies Act, 2014.
As a result Industrial & Provident societies (mostly these are cooperative ventures between community based groups) cannot:
- Be audit exempt;
- Avail of exemption from consolidation on the grounds of being a ‘small’ group;
- Cannot file abridged accounts; and
- Cannot use Section 1A of FRS 102 there is no concept of ‘small’ in their specific legislation;
- Must always include a Statement of Cash Flows under FRS 102/IFRS.
Statement on Relevant Audit Information – this is a statement required under section 330 of the Companies Act, 2014 where the directors of the company confirm that they have taken all relevant steps to inform the auditors of any relevant audit information and have established that the company’s statutory auditors are aware of that information. There is no equivalent requirement in the Industrial & Provident Societies Acts 1893 to 2021.
Compliance Statement – the Directors’ Compliance Statement (section 225 Companies Act, 2014) is required by certain entities incorporated under the Companies Act, 2014 but here is no equivalent in the Industrial & Provident Societies Acts 1893 to 2021.
There was a Government consultation to modernise the laws about Co-operative Societies which ended in February 2022 followed by a bill published in November 2022 but the bill hasn’t progressed as yet. See the Chartered Accountants Ireland website for the latest information available.
IT Controls Assessment
Auditors are reminded that there are relatively significant changes in the requirements of ISA 315 Identifying and Assessing the Risks of Material Misstatement for accounting periods commencing 15 December 2021, which in practical terms means, accounting periods Ended 31 December 2022 and later.
Auditors dealing with the audits of entities with such accounting periods affected by these change will need, to adopt new audit programmes and, in additional to the normal audit tests, to also assess the entity’s IT controls (no matter what the size of that entity).
This is a significant new development for auditors of SMEs, in particular, and will be a game changer ion the type of audit documentation and evidence of assessment of such IT controls by the auditor on audit files.
For an easy to implement additional (two page) IT Controls Questionnaire to help document the above process, please click on this link to download immediately for only €60 + VAT.
Please also go to our website to see our:
- Anti-Money Laundering Policies Controls & Procedures Manual (March 2022) – View the Table of Contents click here.
- AML webinar (March 2022) available here, which accompanies the AML Manual. It explains the current legal AML reporting position for accountancy firms and includes a quiz. Upon completion, you receive a CPD Certificate of attendance in your inbox.
- letters of engagement and similar templates. Please visit our site here where immediate downloads are available in Word format. A bulk discount is available for orders of five or more items if bought together.
- ISQM TOOLKIT or if you prefer to chat through the different audit risks and potential appropriate responses presented by this new standard, please contact John McCarthy FCA by e-mail at john@jmcc.ie.
We typically tailor ISQM training and brainstorming sessions to suit your firm’s unique requirements. The ISQM TOOLKIT 2022 is available to purchase here.

by John McCarthy Consulting Ltd. | Nov 1, 2023 | Blog, News
The UK Economic Crime and Corporate Transparency Act, 2023 become law on 26 October 2023 (all 389 pages of it!). The Act is not expected to become effective until early 2024. It makes the following changes:
- ID with be required (for the first time) for all new/existing company directors, people with significant control (PSC) or beneficial owners as we in them in the RoI), and those who file on behalf of companies;
- There are new rules for registered office addresses which means companies can no longer use a PO Box as their registered office address;
- a new requirement for companies to supply a registered email address;
- a requirement for companies to confirm they’re forming the company for a lawful purpose when they incorporate/confirm on annual renewal in subsequent years.
IT Controls Assessment
Auditors are reminded that there are relatively significant changes in the requirements of ISA 315 Identifying and Assessing the Risks of Material Misstatement for accounting periods commencing 15 December 2021, which in practical terms means, accounting periods Ended 31 December 2022 and later.
Auditors dealing with the audits of entities with such accounting periods affected by these change will need, to adopt new audit programmes and, in additional to the normal audit tests, to also assess the entity’s IT controls (no matter what the size of that entity).
This is a significant new development for auditors of SMEs, in particular, and will be a game changer ion the type of audit documentation and evidence of assessment of such IT controls by the auditor on audit files.
For an easy to implement additional (two page) IT Controls Questionnaire to help document the above process, please click on this link to download immediately for only €60 + VAT.
Please also go to our website to see our:
- Anti-Money Laundering Policies Controls & Procedures Manual (March 2022) – View the Table of Contents click here.
- AML webinar (March 2022) available here, which accompanies the AML Manual. It explains the current legal AML reporting position for accountancy firms and includes a quiz. Upon completion, you receive a CPD Certificate of attendance in your inbox.
- letters of engagement and similar templates. Please visit our site here where immediate downloads are available in Word format. A bulk discount is available for orders of five or more items if bought together.
- ISQM TOOLKIT or if you prefer to chat through the different audit risks and potential appropriate responses presented by this new standard, please contact John McCarthy FCA by e-mail at john@jmcc.ie.
We typically tailor ISQM training and brainstorming sessions to suit your firm’s unique requirements. The ISQM TOOLKIT 2022 is available to purchase here.

by John McCarthy Consulting Ltd. | Oct 17, 2023 | Blog, News
The IAASA Ethical Standard for Auditors (Ireland) 2020 (the Standard) became effective on 15 July 2021. This blog addresses the main requirements of the Standard in so far as it applies to auditors of non-listed private entities.
It is the purpose of this blog to address issues affecting non-listed/private entities. Please refer to the Irish Audit & Accounting Supervisory Authority Ethical Standard 2020 if your interest is in Public Interest/Listed Entities and firms that are part of international networks.
Fee Dependence
Section 4 of the Standard sets percentage limits on the proportion of total fee income that can be earned from an audited entity. These limits are often referred to as ‘fee dependence’. The limits may be exceeded in certain circumstances, without triggering negative consequences. It’s of great importance to keep a record of when these limits are exceeded, for which clients and to maintain a log of the corrective action taken, when the limits are exceeded.
Where it is expected that the total fees for services receivable from a non-listed entity that is not a public interest entity and its subsidiaries relevant to a recurring engagement by the firm will regularly exceed 15% of the annual fee income of the firm or, where profits are not shared on a firm-wide basis, of the part of the firm by reference to which the engagement partner’s profit share is calculated, the firm shall not act as the provider of the engagement for that entity and shall either resign or not stand for reappointment, as appropriate.
Time to resign or expand
Where the total annual fees for audit and non-audit services regularly (defined below) exceed 15% of the firm’s annual fee income, the firm must not accept/continue the audit appointment. Obviously advance planning is required when this situation is on the horizon e.g. expand the firm through merger, so as to dilute the fee dependency position below the 15% threshold or plan to resign. (IAASA Ethical Standard paragraph 4.36).
Between 10% and 15%
Whether or not the limits can be exceeded, depends on certain specific circumstances. Detailed guidance can be found in paragraphs 4.36 to 4.46 of the standard. We pay special attention to the word ‘regularly.’
For non-listed private entities the fee dependence limit is 10%. Where fees for the entity and its subsidiaries regularly exceed 10% of the firm’s annual fee income, but fall below 15%, the firm may determine it is possible to continue to act subject to:
- disclosure to the firm’s Ethics Partner/Function;
- disclosure to those charged with governance of the audit entity; and
- completion of an external independent quality control review prior to the finalisation of the audit report (IAASA Ethical Standard paragraph 4.43).
The table below summarises the fee dependency levels discussed above.
| Type of client |
Normally
acceptable |
Further action required |
Unacceptable if regular |
| Non listed/private entities |
Not more than 10% |
More than 10% but not exceeding 15% |
Exceeding 15% |
Definitions:
Definitions in the area of ethics and audit are often of critical importance to reaching the correct answer. Here is a list of the main definitions that apply:
Firm’s Annual Fee Income – this is the annual fee income as billed by the firm for the provision of services but excludes income where the firm acts as agent for another party (e.g. if the firm is a subcontractor).
Sole practitioners – The limits may be more difficult for a sole practitioner to apply, but the Standard helpfully includes a footnote to paragraph 4.34 confirming that as a sole practitioner, annual fee income includes all earned income received by the individual. This is because the firm (the sole practice) and the individual are effectively one and the same. Monies received from pensions can also be considered as ‘earned income’ as they arise from past earnings.
Engagement partners – Where the profit share for the engagement partner is derived from only part of the firm, the reference to firm should be taken to mean that part of the firm only.
What Does Regularly Mean? – Although there is no definition in the Standard of the term ‘regularly’ a sensible approach is set out in a 2021 information sheet from the ICAEW (unfortunately available to members only) that states that where income from an audited entity has exceeded the limits for three consecutive years, it has become a ‘regular’ event. In such circumstances it would be difficult to argue that it would be acceptable to continue to act.
Special Circumstances – There are some limited circumstances in which the fee limits may be exceeded such as:
- Engagements assigned by legislation – The fee dependence limits do not apply to engagements of entities where the responsibility for the engagement is assigned by legislation and the firm cannot resign from the engagement, irrespective of considerations of economic dependence (e.g. for certain public sector bodies) (IAASA Ethical Standard paragraph 4.33).
- Unpredictable events – Where fee limits are exceeded as the result of an unpredicted individual event or engagement and an objective, reasonable and informed third party would consider ceasing to act as detrimental or against the public interest, the firm may be able to continue subject to disclosure and adequate safeguards (IAASA Ethical Standard paragraph 4.38).
- Starting a new practice – A new firm seeking to establish itself may find it difficult to comply with the fee limits. For a period not exceeding two years, a firm may exceed the 15% limit for non-listed audited entities which are not PIEs, subject to an external independent quality control review before the audit report is issued (IAASA Ethical Standard paragraph 4.44).
- Small entities – For small entities the firm may be able to claim the relief given in paragraph 6.5 of the IAASA Ethical Standard Provisions Available for Audits of Small Entities (PAASE) and dispense with the need for an external review provided the disclosure required by paragraph 6.5 is made. See paragraph 6.4 of the IAASA Ethical Standard for a definition of what constitutes a ‘small entity’.
IT Controls Assessment
Auditors are reminded that there are relatively significant changes in the requirements of ISA 315 Identifying and Assessing the Risks of Material Misstatement for accounting periods commencing 15 December 2021, which in practical terms means, accounting periods Ended 31 December 2022 and later.
Auditors dealing with the audits of entities with such accounting periods affected by these change will need, to adopt new audit programmes and, in additional to the normal audit tests, to also assess the entity’s IT controls (no matter what the size of that entity).
This is a significant new development for auditors of SMEs, in particular, and will be a game changer ion the type of audit documentation and evidence of assessment of such IT controls by the auditor on audit files.
For an easy to implement additional (two page) IT Controls Questionnaire to help document the above process, please click on this link to download immediately for only €60 + VAT.
Please also go to our website to see our:
- Anti-Money Laundering Policies Controls & Procedures Manual (March 2022) – View the Table of Contents click here.
- AML webinar (March 2022) available here, which accompanies the AML Manual. It explains the current legal AML reporting position for accountancy firms and includes a quiz. Upon completion, you receive a CPD Certificate of attendance in your inbox.
- letters of engagement and similar templates. Please visit our site here where immediate downloads are available in Word format. A bulk discount is available for orders of five or more items if bought together.
- ISQM TOOLKIT or if you prefer to chat through the different audit risks and potential appropriate responses presented by this new standard, please contact John McCarthy FCA by e-mail at john@jmcc.ie.
We typically tailor ISQM training and brainstorming sessions to suit your firm’s unique requirements. The ISQM TOOLKIT 2022 is available to purchase here.

by John McCarthy Consulting Ltd. | Oct 14, 2023 | Blog, News
Continuing from last week’s blog we are looking at the guidance issued in ISA 240 ‘The Auditor’s Responsibilities Relating to Fraud in an Audit of Financial Statements’
I
Continuing the items to be documented by the audit engagement team in their discussion of how fraud might be perpetrated in the audit client. That discussion needs to be structured around these headline items (continued from last week):
- Whether there are economic, industry and operating conditions that give rise to fraud risk factors for particular classes of transactions, account balances and disclosures. (Examples of economic, industry and operating conditions that may give rise to fraud risk factors are included in the examples of incentives/pressures and opportunities in Appendix 1.)
- A consideration of any material frauds of which team members have experience in companies in the same industry and whether there are similar risks – see our blog of 3 October about the Protected Disclosures
- A consideration of management’s involvement in overseeing employees with access to cash or other assets susceptible to misappropriation.
- A consideration of any unusual or unexplained changes in behavior or lifestyle of management or employees which have come to the attention of the engagement
- An emphasis on the importance of maintaining a proper state of mind throughout the audit regarding the potential for material misstatement due to fraud.
- A consideration of the types of circumstances that, if encountered, might indicate the possibility of fraud.
- A consideration of how an element of unpredictability will be incorporated into the nature, timing and extent of the audit procedures to be performed.
- A consideration of the audit procedures that might be selected to respond to the susceptibility of the entity’s financial statement to material misstatement due to fraud and whether certain types of audit procedures are more effective than
- A consideration of any allegations of fraud that have come to the auditor’s
- A consideration of the risk of management override of controls.
- A consideration of the extent of segregation of duties and whether and how that may be overridden.
- A consideration of how those charged with governance and management promote a culture of honesty and integrity; what policies they have to facilitate and encourage reporting of wrongdoing (see the Protected Disclosures regime mentioned above); and how they respond to any such reports.
- A consideration of audit team experience, or other knowledge, of the competencies and attitudes of employees in areas where there are risks of material misstatement.
- Circumstances where it may be beneficial to have further discussion(s) among the engagement team at later stages in the audit may include, for example, when the auditor’s evaluation of audit evidence has provided further insight about the risks of material misstatement due to fraud (see more in ISA 240 paragraph A50) or members of the audit team have identified:
- Fraud risk factors that were not covered in the original discussion.
- Actual or suspected fraud.
Further guidance on these topics is given in Application paragraphs A12 and A12-1 in the standard.
IT Controls Assessment
Auditors are reminded that there are relatively significant changes in the requirements of ISA 315 Identifying and Assessing the Risks of Material Misstatement for accounting periods commencing 15 December 2021, which in practical terms means, accounting periods Ended 31 December 2022 and later.
Auditors dealing with the audits of entities with such accounting periods affected by these change will need, to adopt new audit programmes and, in additional to the normal audit tests, to also assess the entity’s IT controls (no matter what the size of that entity).
This is a significant new development for auditors of SMEs, in particular, and will be a game changer ion the type of audit documentation and evidence of assessment of such IT controls by the auditor on audit files.
For an easy to implement additional (two page) IT Controls Questionnaire to help document the above process, please click on this link to download immediately for only €60 + VAT.
Please also go to our website to see our:
- Anti-Money Laundering Policies Controls & Procedures Manual (March 2022) – View the Table of Contents click here.
- AML webinar (March 2022) available here, which accompanies the AML Manual. It explains the current legal AML reporting position for accountancy firms and includes a quiz. Upon completion, you receive a CPD Certificate of attendance in your inbox.
- letters of engagement and similar templates. Please visit our site here where immediate downloads are available in Word format. A bulk discount is available for orders of five or more items if bought together.
- ISQM TOOLKIT or if you prefer to chat through the different audit risks and potential appropriate responses presented by this new standard, please contact John McCarthy FCA by e-mail at john@jmcc.ie.
We typically tailor ISQM training and brainstorming sessions to suit your firm’s unique requirements. The ISQM TOOLKIT 2022 is available to purchase here.

by John McCarthy Consulting Ltd. | Sep 20, 2023 | Blog, News
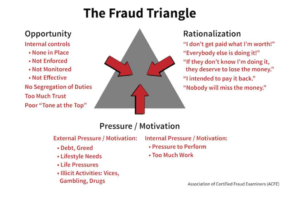
The ‘fraud triangle’ (shown below) is a well-known tool for enabling discussions among audit teams about the possible ‘climatic’ factors that may be present in an audit client. Where all three coincide, fraud is much more likely to be present.

ISA 240 ‘The Auditor’s Responsibilities Relating to Fraud in an Audit of Financial Statements’ was re-issued in October 2022 with additional requirements (among other topics) to do with the audit engagement team discussion.
For the purposes of this blog (Part 1 of a 2 part series) we are focusing on the main areas of the audit team discussion.
‘The discussion shall include an exchange of ideas among engagement team members about fraud risk factors, including:
- incentives for management or others within the entity to commit fraud;
- how management could perpetrate and conceal fraudulent financial reporting; and
- how assets of the entity could be misappropriated (ISA 240.16.1)
For a group audit, the discussion among the group engagement team shall include matters to discuss with the component auditor of a significant component about the susceptibility of the component to material misstatement of the financial information of that component due to fraud. (ISA 240.16.2)
If allegations of fraud come to the auditor’s attention, the discussion shall include how to investigate and respond to those allegations. (ISA 240.16.3) see last week’s blog on the expanded Protected Disclosures regime now in force in Ireland and which will have implications for auditors of the affected entities.
The standard allows for the initial engagement team discussion to be later revisited and revised, where necessary, when ‘fraud risk factors that have been identified during the course of the audit and the implications for the audit’ considered (ISA 240.16.4)
Basically the audit engagement team is expected to document a discussion of how fraud might be perpetrated in the audit client. That discussion needs to be structured around the headline items shown below:
The guidance focuses on:
- incentives to manage earnings or key performance indicators derived from the financial statements in order to deceive financial statement users by influencing their perceptions as to the entity’s performance and profitability;
- A consideration of circumstances that might be indicative of earnings management and the practices that might be followed by management to manage earnings that could lead to fraudulent financial reporting.
- A consideration of the risk that management may attempt to present disclosures in a manner that may obscure a proper understanding of the matters disclosed (for example, by including too much immaterial information or by using unclear or ambiguous language).
- A consideration of the known external/internal factors affecting the entity that may create an incentive or pressure for management or others to commit fraud, provide the opportunity for fraud to be perpetrated, and indicate a culture or environment that enables management or others to rationalize committing
Further guidance on these topics is given in Application paragraphs A12 and A12-1 in the standard. We will say more about this topic next week.
IT Controls Assessment
Auditors are reminded that there are relatively significant changes in the requirements of ISA 315 Identifying And Assessing The Risks Of Material Misstatement for accounting periods commencing 15 December 2021, which in practical terms means, accounting periods Ended 31 December 2022 and later.
Auditors dealing with the audits of entities with such accounting periods affected by these change will need, to adopt new audit programmes and, in additional to the normal audit tests, to also assess the entity’s IT controls (no ,matter what the size of that entity).
This is a significant new development for auditors of SMEs, in particular, and will be a game changer ion the type of audit documentation and evidence of assessment of such IT controls by the auditor on audit files.
For an easy to implement additional (two page) IT Controls Questionnaire to help document the above process, please click on this link to download immediately for only €60 + VAT.
Please go to our website to see our:
- letters of engagement and similar templates. Please visit our site here where immediate downloads are available in Word format. A bulk discount is available for orders of five or more items if bought together.
- ISQM TOOLKIT or if you prefer to chat through the different audit risks and potential appropriate responses presented by this new standard, please contact John McCarthy FCA by e-mail at john@jmcc.ie.
We typically tailor ISQM training and brainstorming sessions to suit your firm’s unique requirements. The ISQM TOOLKIT 2022 is available to purchase here.

by John McCarthy Consulting Ltd. | Sep 20, 2023 | Blog, News
The Protected Disclosures (Amendment) Act 2022 (the Act) requires certain entities to have in place procedures to establish internal reporting channels and procedures to enable workers make protected disclosures (defined as a ‘relevant wrongdoing’). From 17 December 2023 its scope will be expanded to employers with over 50 employees.
The Act already applies to certain entities from 1 January 2023 including entities employing over 250 employees and certain financial services (regardless of employee numbers) entities like AIFMs, MiFID firms, Irish UCITS management companies and other Irish financial service providers, as well as Irish domiciled corporate funds.
The 2022 Act expands the scope of the Protected Disclosures Act, 2014 to include areas such as:
- public procurement;
- financial services;
- anti-money laundering (AML);
- product safety and compliance;
- transport safety;
- environmental protection;
- radiation and nuclear safety;
- food and animal health and welfare;
- public health;
- consumer protection; and
- the protection of privacy and personal data.
Its scope is being enhanced from 17 December 2023 when employers with over 50 employees will need to have such a policy in place. The basic steps for employers are:
- the establishment, maintenance and operation of a secure and confidential internal reporting channel for workers who wish to make a protected disclosure, whether in writing, orally or both;
- the designation of an impartial and competent person who may be internal/external; and
- an obligation to provide workers with information on the internal/external protected disclosure reporting process.
The Act also creates a newly established Office of the Protected Disclosures Commissioner (www.opdc.ie) which will forward reports of work-related wrongdoing to the most appropriate body for initial assessment and follow-up.
Employees are given protection from dismissal from employment (among other protections) when they report a ‘relevant wrongdoing’ (defined which are defined to include:
- Where an offence has been or is likely to be committed;
- Non-compliance with a legal obligation – the 2014 Act excludes obligations arising under the worker’s contract of employment;
- A miscarriage of justice;
- Danger to the health and safety of any individual;
- Damage to the environment;
- An unlawful or otherwise improper use of funds or resources of a public body;
- Oppression, gross neglect or gross mismanagement by a public body; and
- Other breaches related to the financial interests of the EU the internal market, EU competition and state aid rules and internal market rules on corporate tax.
The legislation is complex and we cannot cover all its aspects in the space of a blog. We urge our readers to seek independent professional and legal advice where necessary.
IT Controls Assessment
Auditors are reminded that there are relatively significant changes in the requirements of ISA 315 Identifying And Assessing The Risks Of Material Misstatement for accounting periods commencing 15 December 2021, which in practical terms means, accounting periods Ended 21 December 2022 and later.
Auditors dealing with the audits of entities with such accounting periods affected by these change will need, to adopt new audit programmes and, in additional to the normal audit tests, to also assess the entity’s IT controls (no ,matter what the size of that entity).
This is a significant new development for auditors of SMEs, in particular, and will be a game changer ion the type of audit documentation and evidence of assessment of such IT controls by the auditor on audit files.
For an easy to implement additional (two page) IT Controls Questionnaire to help document the above process, please click on this link to download immediately for only €60 + VAT.
Please go to our website to see our:
- letters of engagement and similar templates. Please visit our site here where immediate downloads are available in Word format. A bulk discount is available for orders of five or more items if bought together.
- ISQM TOOLKIT or if you prefer to chat through the different audit risks and potential appropriate responses presented by this new standard, please contact John McCarthy FCA by e-mail at john@jmcc.ie.
We typically tailor ISQM training and brainstorming sessions to suit your firm’s unique requirements. The ISQM TOOLKIT 2022 is available to purchase here.












